Bariatric Surgery For Weight Loss
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that in 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight and of these, over 650 million were obese. Obesity has been linked to more deaths worldwide and a reduction in a person’s life expectancy because it contributes to 44% of diabetes and 23% of ischaemic heart disease. It is estimated that a person with obesity, will have a 7-year shorter life expectancy than the normal population.
Bariatric surgery (also known as weight-loss surgery or metabolic surgery), is an operation on digestive system for those with a body mass index (BMI) of over 40 and for those with weight-related co-morbidities with a BMI of 35-40. The American Diabetes Association Guidelines also suggested those poorly controlled diabetics with Class I obesity (BMI 27.5-32.5) to consider surgery.
Types of Bariatric Surgery

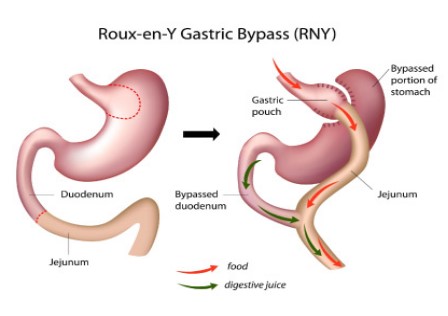

The most common bariatric procedures performed are the sleeve gastrectomy, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and mini gastric bypass which can be done using laparoscopic technique (also known as key-hole surgery). The choice of procedure takes into account certain factors such as age, risk profile, access to follow-up and monitoring, previous interventions and lifestyle interventions. Your surgeon will be the best person to discuss these options with you.
Expected Benefits
The success rate and the Effective Weight Loss (EWL) depends on the patient’s commitment to
- change of lifestyle to include regular exercise and dietary changes
- following your dietician or nutritionist dietary program before & after the surgery (click to read)
- regular follow-ups with your doctor and/or dietician
Disclaimer. TELEME blog posts contains general information about health conditions and treatments. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. The information is not advice and should not be treated as such. If you think you may be suffering from any medical condition, you should seek immediate medical attention from your doctor or other professional healthcare providers. You should never delay seeking medical advice, disregard medical advice, or discontinue medical treatment because of information on this website.
Disclaimer. TELEME blog posts contains general information about health conditions and treatments. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. The information is not advice and should not be treated as such.
If you think you may be suffering from any medical condition, you should seek immediate medical attention from your doctor or other professional healthcare providers. You should never delay seeking medical advice, disregard medical advice, or discontinue medical treatment because of information on this website.