NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the term for a range of conditions caused by the built up of fat in the liver. A healthy liver should contain little or no fat. Early stage NAFLD does not usually cause any harm, but can lead to serious liver damage if it gets worse. Having high level of fats in your liver is associated with an increased risk of diabetes, heart attacks and strokes, again pointing towards metabolic syndrome. If detected and managed at an early stage it is possible to prevent the progression and even reverse the process.
Stages of NAFLD
NAFLD develops in four main stages. Most people will only develop the first stage though some will progress if they have a poor lifestyle.
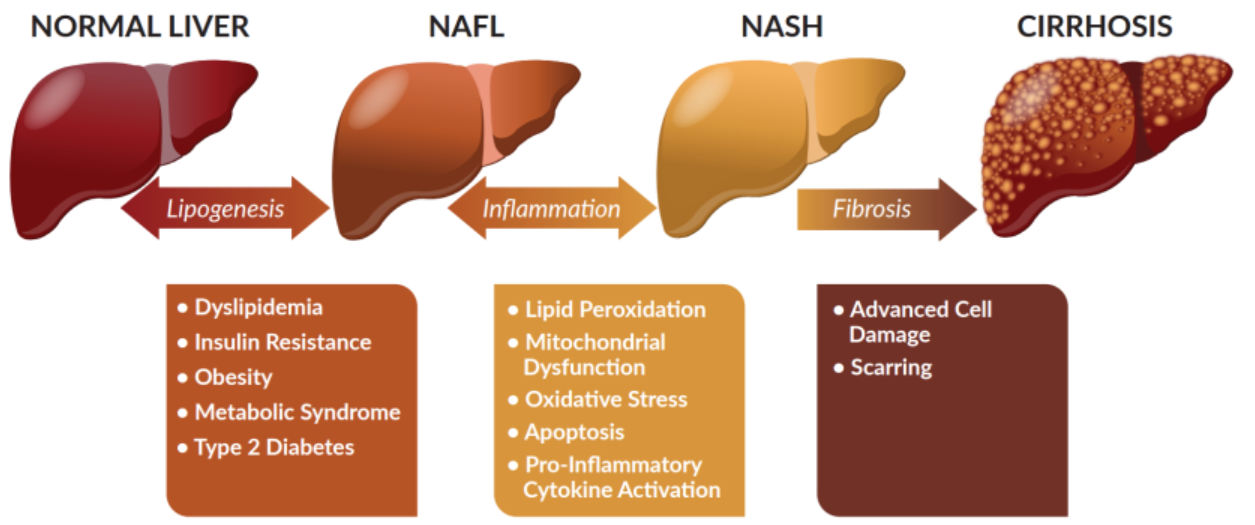
Stage 1 – Simple fatty liver (steatohepatitis) is a largely harmless buildup of fat in the liver cells that is usually only diagnosed during tests carried out for another reason.
Stage 2 – Non- alcoholic steatohepatitis is a more serious form of NAFLD where the liver has become inflamed.
Stage 3 – Fibrosis where persistent inflammation causes scar tissue around the liver and nearby blood vessels, but the liver is still able to function normally.
Stage 4 – Cirrhosis which is the most serious stage, occurring after years of inflammation, where the liver shrinks and becomes scarred. This damage is permanent and can lead to liver failure and liver cancer.
Symptoms of NAFLD
Usually there are no symptoms. Some might complain of dull ache over top right of the abdomen, generalized lethargy, weakness and weight loss. If cirrhosis develops than signs and symptoms of liver failure are seen.
Diagnosis of NAFLD
Usually a routine blood test for liver function or ultrasound scan of the liver might pick up fatty liver.
Treatment of NAFLD
Basically this is lifestyle change.

- Lose weight – Losing 10% of your fat will remove the fat from your liver and reduce the inflammation. Reducing abdominal girth and total body fat is important.
- Eat a healthy diet – Eat real food. Avoid refined carbohydrates and empty calorie foods. Sugars especially refined sugars increase inflammation. Also avoid preserved meats and processed foods. Also try eating smaller portions of food.
- Exercise regularly – Aerobic exercise like walking and cycling is good but any exercise is beneficial. The idea is just move.
- Stop smoking – This can cause overall inflammation and together with NAFLD is a risk factor for heart attacks and strokes.
- Avoid alcohol – Alcohol is the other important cause of inflammation of the liver and should be avoided to prevent further damage to the liver.
Disclaimer. TELEME blog posts contains general information about health conditions and treatments. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. The information is not advice and should not be treated as such.
If you think you may be suffering from any medical condition, you should seek immediate medical attention from your doctor or other professional healthcare providers. You should never delay seeking medical advice, disregard medical advice, or discontinue medical treatment because of information on this website.