Bladder Cancer – Tests & Diagnosis
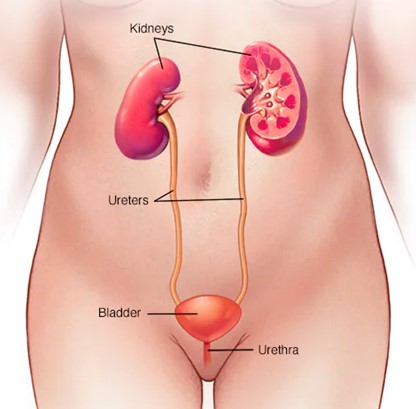
The bladder is a muscular organ which holds and stores the urine produced by the kidneys so that you can decide to pass urine at a convenient time and place. It can store up to x litres of urine before it becomes full.
Risk factors for developing Bladder Cancer
Smoking and exposure to chemicals used in industrial production of plastics, rubber products or leather increases the risk of bladder cancer. Other risk factors include age (most bladder cancers occur in people over 65 years old), family history of bladder cancer and chronic bladder infection.
Click to view John Hopkins Medicine video on Bladder Cancer Guide
Symptoms
There may not be any symptoms during the early stages of bladder cancer. These are the common symptoms for which you MUST see a urologist for a check up
- Blood in the urine (haematuria)
- Frequent urination or urgency to pass urine
- Pain when you pass urine
- Back, lower abdomen or pelvic pain
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of bladder cancer involves;
- Urine testing and cytology (looking for cancer cells in the urine)
- CT or MRI scan (to look for cancer spread and determine the cancer stage
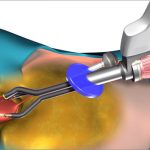
- Blue light cystoscopic examination of the lesion
- Transurethral biopsy and/or resection of the tumour (TURBT)
Click to view Urology Care Foundation video on TURBT
Possible Risks of TURBT
- Bleeding for the first few days
- Urinary tract infection
- Bladder wall perforation
- Bladder scarring
- Loss of bladder control and urinary incontinence
See a Urologist if you have any urinary issues
Disclaimer. TELEME blog posts contains general information about health conditions and treatments. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. The information is not advice and should not be treated as such.
If you think you may be suffering from any medical condition, you should seek immediate medical attention from your doctor or other professional healthcare providers. You should never delay seeking medical advice, disregard medical advice, or discontinue medical treatment because of information on this website.