Monkeypox, renamed as Mpox, is a rare but potentially serious viral illness. It is a zoonotic disease, which means it spreads from animals to humans. Scientists first identified it in 1958 in monkeys kept for research, giving the disease its name. The first human case occurred in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Since then, we’ve seen cases in several African countries and more recently, in other parts of the world. Although similar to smallpox, monkeypox is generally less severe with milder symptoms.
Symptoms
You’ll typically notice monkeypox symptoms 5 to 21 days after exposure to the virus. The illness usually begins with:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Back pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Chills
- Fatigue
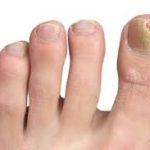
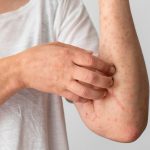
Within 1 to 3 days after your fever starts, you might develop a rash. This rash often begins on your face and then spreads to other parts of your body. The rash goes through several stages, from flat spots to raised bumps, then fluid-filled blisters, and finally scabs that fall off.
Risk Factors for Virus Spread or Transmission
Monkeypox spreads primarily through close contact with an infected person or animal. Here’s how the virus usually spreads:
- Bites, scratches, or direct contact with body fluids of an infected animal
- Close contact with infected people or items used by an infected person
Management of Monkeypox
While there’s NO specific antiviral treatment approved specifically for monkeypox, most cases are mild and resolve on their own within 2 to 4 weeks. However, supportive care is crucial to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Here’s what treatment typically involves:
- Symptom Management:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage fever, headaches, and muscle aches.
- Staying well-hydrated is essential, especially if you have a fever or are experiencing symptoms like sore throat or difficulty swallowing.
- Keep the rash clean and dry. If needed, topical treatments may be prescribed to prevent secondary bacterial infections of the skin lesions.
- Isolation:
- Symptoms can often be managed at home, however, limit contact with household members and use separate bedding, towels, and utensils.
- Antiviral Treatments:
- Healthcare providers might consider antivirals if a patient has a compromised immune system.
- Vaccination Post-Exposure:
- If you’ve been exposed to monkeypox, getting vaccinated with a smallpox vaccine within 4 days of exposure may prevent the onset of the disease or reduce its severity. In some cases, vaccination up to 14 days after exposure can still provide benefits.
- Monitoring for Complications:
- Watch for signs of secondary bacterial infections in the skin lesions, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus. These require prompt medical attention and possibly antibiotics.
- If the virus spreads to the lungs or causes severe respiratory symptoms, immediate medical care is necessary.
Prevention
- Practice Good Hygiene
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) when treating or caring for someone with monkeypox
- Get Vaccinated
Discuss the treatment options with your doctor.
Disclaimer. TELEME blog posts contains general information about health conditions and treatments. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. The information is not advice and should not be treated as such.
If you think you may be suffering from any medical condition, you should seek immediate medical attention from your doctor or other professional healthcare providers. You should never delay seeking medical advice, disregard medical advice, or discontinue medical treatment because of information on this website.